Melasma Treatment: Causes, Symptoms, Types, Diagnose, Treatment & Prevention Tips
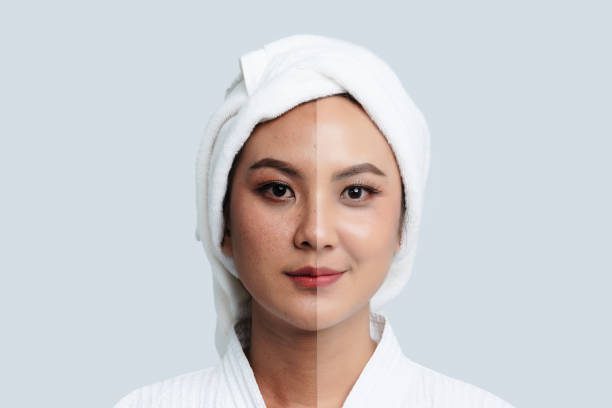
Melasma is a pigmentation disorder that affects the skin’s tone and appearance and may lead to premature ageing in adult women. It is a benign skin disease, but its chronicity and persistence can often make it challenging to treat.
However, experienced dermatologists at Oliva excel in treating different pigmentary concerns, including melasma, using revolutionary USFDA-approved methods with proven safety and efficacy to help you regain your flawless complexion. Read on to know more about the melasma treatment procedure, results, cost and more!
What Is Melasma?
Melasma is a skin disease that leads to the appearance of flat brownish or blue-grey patches on the skin, especially on the face. It affects adults and is a more common complaint among women than men. Chloasma or mask of pregnancy is another name for melasma. Sun exposure is a common risk factor. Melasma is a chronic pigmentary disorder that waxes and wanes but often remains resistant to treatment.
Where Does Melasma Commonly Occur?
Melasma occurs most commonly on the face, including:
- Cheeks
- Forehead
- Bridge of nose
- Chin
Apart from the face, it rarely involves the exposed skin of the forearms, neck and back.
What Are The Types Of Melasma?
Dermatologists categorise the types of melasma based on the depth of the skin discolouration:
- Epidermal Melasma: The melanin deposit in the topmost layer of skin, i.e., the epidermis, leads to dark brown patches with well-defined borders. This superficial type of melasma responds best to treatment.
- Dermal Melasma: The pigment build-up in the dermis, the deeper layer of skin, is not easily accessible. It leads to the appearance of light brown or bluish-grey diffused patches that respond poorly to treatment.
- Mixed Melasma: This pigmentary concern causes different colour patches in the epidermis and dermis. This is the most common type of melasma, and the treatment response usually varies depending on the amount and location of the melanin build-up.
Signs And Symptoms Of Melasma
The signs and symptoms of melasma include:
- Freckle-like spots
- Flat patches of brown, blue or grey colour
- Defined or diffused patches
The patches usually occur symmetrically on the cheeks, forehead, nose, chin and jawline.
What Causes Melasma?
Here are two primary causes of melasma:
- Sun/UV Exposure: Exposure to UV radiation from the sun or laptop/TV screens can trigger excess melanin production in the skin. It can worsen melasma if present or cause recurrence after treatment.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Dermatologists often correlate melasma cases with estrogen and progesterone sensitivity. Melasma is significantly more common in pregnant women and those using high-dose hormonal contraceptive pills. Hormonal changes during menopause or conditions like hypothyroidism can often cause or worsen melasma.
Apart from these, a few other factors may trigger melasma:
- Family History: Those with a positive history of melasma in the family have a higher risk than others.
- Skin Colour: People with dark skin are more likely to develop melasma than those who are fairer.
- Chemical-based Skin Care Products: Skin-care products with fragrances and chemicals that cause skin irritation can trigger melasma.
How To Diagnose Melasma?
Dermatologists at Oliva diagnose melasma by clinically examining the discoloured skin.
They may use Wood’s lamp method to observe the skin under blue light to identify the pigmentation level. In exceptional cases, they may perform a biopsy in the affected area to confirm the diagnosis under a microscope.
What Is The Treatment For Melasma?
Although many advanced treatments are available, the response of melasma to treatments remains variable. No single treatment option can ensure a total and permanent relief from melasma.
At Oliva, your doctor will customise your treatment and recommend regular maintenance to reduce melasma and prevent a recurrence. She may recommend any of the following options as standalone or combo treatment based on the type, cause and severity of your skin condition:
- Topical or Oral Medications: Medications, especially topical creams, are often the first line of treatment and an essential part of post-care. It may include:
- Hydroquinone: Your dermatologist at Oliva may recommend hydroquinone with a concentration of 2-4% as the primary treatment for melasma. She may advise you to apply it at night on the patches for 3-4 months. Prolonged use may aggravate pigmentation.
- Retinoids: Medical experts often use tretinoin in conjunction with hydroquinone or other bleaching agents at night to boost the results of melasma treatment.
- Bleaching Agents: Skin lightening agents like kojic acid, azelaic aid, glycolic acid, arbutin and Vitamin C can reduce melanin synthesis and help lighten the pigmented patches. Your doctor may add it to your post-care regimen as long-term maintenance therapy to minimise the chances of recurrence of melasma.
- Tranexamic Acid: A newer molecule used in oral, injectable or topical form by leading dermatologists for treating melasma is quite effective and may be a part of a combination treatment.
- Hormonal Medications: Your dermatologist may assess your hormonal health and advise you to discontinue any medication that may induce melasma.
- Advanced Procedural Treatments: Here are some in-clinic treatments that your dermatologist at Oliva may recommend for attaining visible results of melasma treatment.
- Chemical Peels: The application of different concentrations of natural extracts like glycolic acid and kojic acid on the discoloured skin for controlled exfoliation of top layers inhibits melanin formation. It is most effective in reducing epidermal melasma. However, you may need multiple sessions of chemical peels treatment at regular intervals of a few weeks to attain visible results.
- Laser Treatment: Dermatologists at Oliva undergo rigorous training to use the latest USFDA-approved Q-switched Nd:YAG laser technology and treat deeper melasma that does not respond to topical medication and peel treatment. The laser beam penetrates the deeper layers to break down the excess melanin without adversely affecting the surrounding skin. However, the precise treatment may require multiple sessions based on the type and severity of your skin condition to provide the best results and for regular maintenance.
Remember, preventing exposure to UV rays is the most crucial step in treating melasma, as even mild sun damage can increase, trigger or cause recurrence. It is mandatory to use sun protection with every treatment modality.
How To Prevent Melasma?
Unfortunately, there is no sure-shot way to prevent melasma altogether. However, the following measures can reduce the risk of melasma and recurrence:
- Avoid Excessive Sun Exposure: Do not go out during peak sunlight hours or use protective gear like scarves, sunglasses and umbrellas to prevent melasma and other forms of sun damage to the skin.
- Regular Use Of Sunscreen: Use sunscreen with SPF 30 or above recommended by your dermatologist 15-20 minutes before going out in the sun. Reapply every three hours to prevent melasma and lighten existing pigmentary conditions.
- Healthy Diet And Skin-Care Habits: A nutrient-rich diet with vitamin D and regular skin-care helps to keep the skin healthy and protect it from multiple disorders, including discolouration.
- Judicious Use Of Hormonal Pills And Contraceptives: Consult a doctor to avoid indiscriminate use of hormonal pills if you have a positive family history of melasma.
Who Is At Risk Of Melasma?
Melasma occurs more in dark-skinned women than men. People with a family history, regular sun exposure and those taking hormonal medicines have increased chances of melasma. Pregnancy can also be a risk factor.
Is Melasma Cancerous?
Melasma is not a sign of cancer, nor can it become malignant in future. However, since skin cancers sometimes cause discolouration, visiting a dermatologist at the earliest is advisable to confirm your diagnosis.
Is Melasma Permanent?
Melasma is a chronic skin discolouration that may fade naturally in pregnancy-induced cases or after treatment, but the risk of future recurrence remains. In some cases, melasma might be permanent and unresponsive to treatment.
Is Melasma Painful?
No, melasma is asymptomatic. There is no pain/itchiness/irritation associated with it.
Do Food Habits Affect Melasma?
No food worsens or causes melasma. However, dermatologists recommend a diet rich in Vitamin D for healthy skin, which may reduce the chances of melasma in the long run.
Can Melasma Appear Overnight?
No, the discoloured patches that appear due to melasma form gradually over months to years.
Are Freckles Same As Melasma?
No, melasma may sometimes start with freckle-like spots, but freckles are not the same as melasma. They have a familial tendency and respond well to treatment.